The following are some of the biggest killer diseases in the developing world which are ranked according to the annual death tolls. Some of these diseases are silent killers because the symptoms do not manifest itself until a later stage.
1. Lower Respiratory Infections
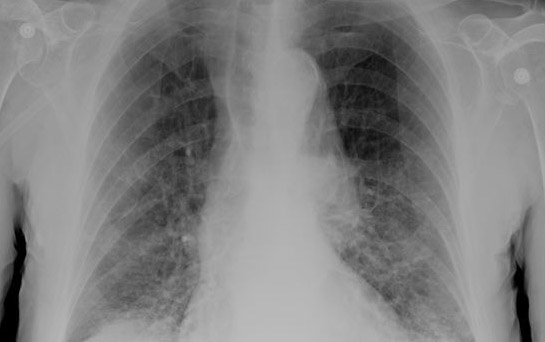 At least more than 4 million people are killed each year by lower respiratory infections such as pneumonia and other diseases of the bronchial tubes, windpipe or lungs, including Legionnaire’s disease. This infection spreads through laughing, exhaling, coughing or sneezing.
At least more than 4 million people are killed each year by lower respiratory infections such as pneumonia and other diseases of the bronchial tubes, windpipe or lungs, including Legionnaire’s disease. This infection spreads through laughing, exhaling, coughing or sneezing.
2. HIV/AIDS
 In 2004, over 3 million deaths were attributed to AIDS. Some 39.4 million people in the world live with HIV. HIV is the abbreviation for “human immunodeficiency virus”. It damages the immune system. HIV infection is the root cause of AIDS, which stands for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome.
In 2004, over 3 million deaths were attributed to AIDS. Some 39.4 million people in the world live with HIV. HIV is the abbreviation for “human immunodeficiency virus”. It damages the immune system. HIV infection is the root cause of AIDS, which stands for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome.
3. Malaria
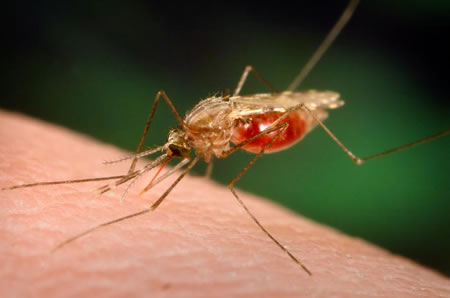 The death toll as a result of malaria is between 1 million and 5 million each year. According to WHO, the number of people affected by Malaria annually is 300 millions. The disease spreads through mosquito infestation.
The death toll as a result of malaria is between 1 million and 5 million each year. According to WHO, the number of people affected by Malaria annually is 300 millions. The disease spreads through mosquito infestation.
4. Diarrhoea
 Diarrhoea kills around 2.2 million people each year. There are at least 4 billion cases of infected people every year. Caused by cholera, dysentery and other scourges, Diarrhoea is a symptom of infection viral, bacterial and parasitic organisms such as microscopic worms. Dehydration causes the maximum amount of diarrhoea-related deaths in children.
Diarrhoea kills around 2.2 million people each year. There are at least 4 billion cases of infected people every year. Caused by cholera, dysentery and other scourges, Diarrhoea is a symptom of infection viral, bacterial and parasitic organisms such as microscopic worms. Dehydration causes the maximum amount of diarrhoea-related deaths in children.
5. Tuberculosis
 Over 2 million people die of TB every year. Over 8 million new cases develop each year and about 2 billion people are infected with TB. A chronic cough, chills, fever, weight loss and weakness are the main symptoms of this disease. The disease spreads through sneezing or coughing. Directly Observed Therapy Short-course – DOTS – is the internationally recommended approach to TB control.
Over 2 million people die of TB every year. Over 8 million new cases develop each year and about 2 billion people are infected with TB. A chronic cough, chills, fever, weight loss and weakness are the main symptoms of this disease. The disease spreads through sneezing or coughing. Directly Observed Therapy Short-course – DOTS – is the internationally recommended approach to TB control.